


The difference between the atomic weight of the element in such specimens and that given in the Table may exceed the stated uncertainty. Molar Mass, Molecular Weight and Elemental Composition Calculator.
Al molar mass full#
The original paper should be consulted for full details of the variation in atomic weight and the half life of the radioisotopes quoted below.Ī number in parentheses indicates the uncertainty in the last digit of the atomic weight. For radioactive elements the isotope with the longest half-life is quoted in parenthesis. In the other lists the values quoted are those suggested for material where the origin of the sample is unknown. The standard atomic weights of twelve elements having two or more stable isotopes have variability of atomic-weight values in natural terrestrial materials. Previous values may be consulted from the 1993 table, the 1995 table, the 1997 table, the 1999 table, the 2001 table, the 2005 table, the 2007 table, the 2009 table, the 2011 table, the 2013 table, the 2015 table or the 2019 table. World Wide Web version of atomic weight data originally prepared by G. These tables are based on the 2021 table with changes from the 2019 table for the values of Ar, Hf, Ir, Pb and Yb and changes to the uncertainty for Al, Au, Co, F, Ho, Mn, Nb, Pa, Pr, Rh, Sc, Tb, Tm, and Y.
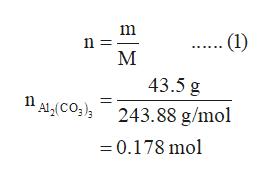
This selective catalyst should be used in the future to qualify the properties of these ROCOP polyesters and to tune (multi)block polymer structures.2021 Atomic Weights IUPAC Commission on Isotopic Abundances and Atomic Weights. It is also enchains phthalic anhydride, vinyl cyclohexene oxide and ε-decalactone, via switchable catalysis, to make high molar mass triblock polyesters (81 kg mol −1, Đ = 1.04). As proof of its potential, high molar mass poly(vinyl cyclohexene oxide- alt-phthalic anhydride) (91 kg mol −1) shows 5× greater flexural strain at break ( ε b = 3.7%) and 9× higher maximum flexural stress ( σ f = 72.3 MPa) than the previously accessed medium molar mass samples (24 kg mol −1). The organometallic heterodinuclear Al( III)/K( I) complex, applied with a diol, is tolerant to a range of epoxides/phthalic anhydride and produces only α,ω-hydroxyl telechelic polyesters with molar masses from 6–91 kg mol −1, in all cases with monomodal distributions. Here, a new type of catalyst for the ring-opening polymerization (ROCOP) of epoxides and anhydrides combines unusually high chain end-group selectivity, fast rates, and good molar mass control. Polyesters are important plastics, elastomers and fibres efficient and selective polymerizations making predictable, high molar mass polymers are required.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
